Harley Flathead Small-Twins and Big-Twins
The flathead engine plays an important role in motorcycle history. It was a substantial improvement over the existing design, the intake-over-exhaust (IOE), which had an intake valve in the cylinder head and the exhaust valve located in the block.

NOTE: Flathead and Side-Valve (SV) are the same type of motor.
Side-Valve Simplicity
Advantages of a flathead engine over an OHV (overhead valve) engine were cost of manufacture and simplicity. With valves positioned in the engine block beside the piston, instead of in the cylinder head as in an OHV engine, push rods and rocker arms were not needed. Cylinder heads need only be a simple casting with threaded holes for the spark plugs.
First Harley Flathead
The flathead motor design was first utilized by Harley-Davidson in single-cylinder form.
D Series (45ci Small-Twin)
The Motor Company introduced their first V-twin flathead, the 750cc D-model, in 1929. It was initially built as a competitor to the Indian flathead 750 V-twin. Suspension was comprised of leading-link forks (springer) and no rear suspension (hardtail).
A unique feature of the D-Model was the generator, which mounted vertically beside the front cylinder, prompting Indian enthusiasts to call it the "3-cylinder Harley."

The Harley D series was produced from 1929 to 1931.
******************************
R Series (45ci Small-Twin)
Frame modifications from the D-Series now allowed use of a more conventional horizontal generator. R-Models included the 45-solo, R, RL, and RLD models. Production ran from 1932 to 1936.
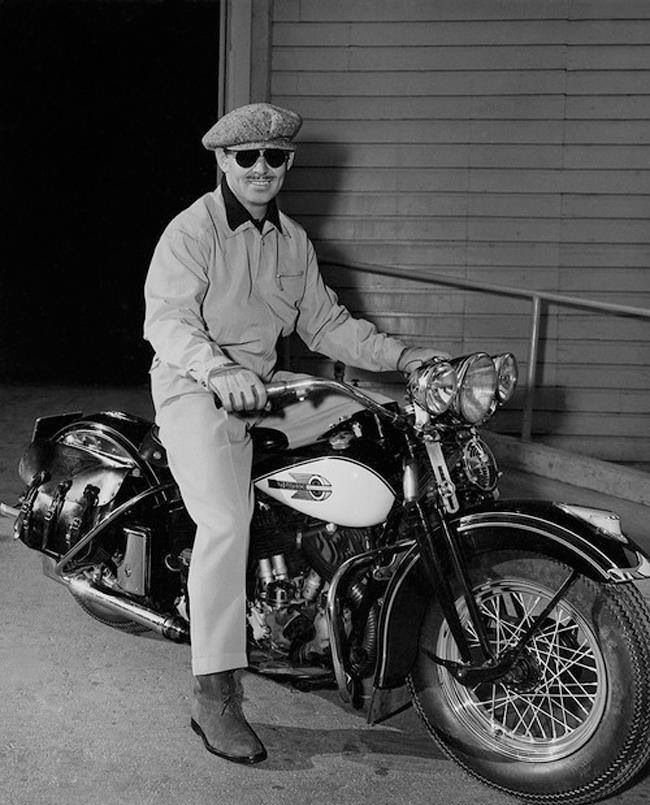

Hollywood movie star Clark Gable owned and rode a 1934 RL45.
Oiling System
Both the DL and RL engines used a total-loss oiling system, and were succeeded in 1937 by the WL series 45, which had recirculating oil lubrication. This significantly improving engine lubrication, cooling, and durability.
******************************
Harley WL (45ci Small-Twin)
The W-series (1937-1952) makes up the majority of Harley V-Twin Flatheads produced, and were the basis for the WLA military bike, WR factory racer, and others.
Harley 45 Articles:
Harley 45 Engine Teardown and Inspection
Harley 45 Engine Build
Harley 45 Engine Assembly
Harley 45 Bottom End Assembly
Harley 45 Cylinder Assembly
Harley 45 Timer And Ignition
Harley 45 Drivetrain
Harley 45 Frame Choices
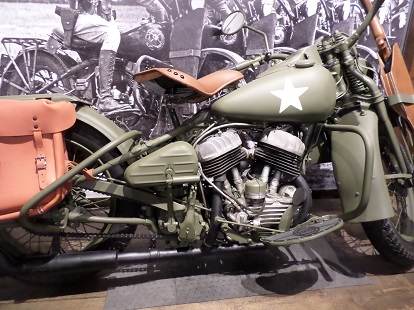
Read: Harley WLA History
When World War II was over, there was a large surplus of WLA bikes, most of them being sold very cheaply. In America, many of these surplus military models became the first modern-day bobbers and choppers.
Rear Brakes
Prior to 1935, Harley 45 Solo models came equipped with external contracting band rear brakes. A mechanical rear drum brake was fitted to all models starting in 1935.

******************************
Servi-Car (G-Series 45)
Built in response to rival Indian's "Dispatch Tow" three- wheeler, the Harley-Davidson Servi-car appeared late in 1931 as a 1932 model. In addition to its intended use for car delivery, the flathead-powered trike has been utilized by police departments, fire houses, postal carriers, and the military.

Produced from 1932 to 1973, every Servi-car left the factory powered by a 45ci flathead engine.

Servi-Car Articles:
Servi-Car Frame Identification and Inspection
Rear Axle Rebuild
Servi-Car Box and Fenders
Gas/Oil Tanks
Servi-Car Rear Brake Overhaul
1961 Servi-Car Project

Read: Servi-Car Exhaust And Why Getting Parts Is So Frustrating
******************************
45 Engine Parts Interchangeability
Pistons, connecting rods, cylinders, and many other parts were the same for all years of Harley 45 motors. One minor difference is that on 1936 and earlier engines, the oil holes and key-ways on the flywheels are different than on later engines.
******************************
Harley Flathead Big-Twins
In 1930, Harley introduced their first Big-Twin flathead, a 74 cubic-inch version.

From 1930 to 1935, Big-Twin Flatheads led the Harley-Davidson line-up. The first VL models were 74 cubic-inches, with an 80ci version (the UL model) added late in 1935.
The 74ci motor had a 3-5/16" bore while the 80ci motor had a 3-7/16" bore.
Harley continued to produce 80" flatheads until 1940, and the 74" flathead was offered until 1948.
Externally, 1938 through 1948 74ci flathead motors have 11-fin cylinders. The 1937 74ci and all 1937 through 1941 80ci motors have 13-fin cylinders. The extra fins are just above the mounting flange.
******************************
Small-Twin vs Big-Twin Harley Flathead
The small-twin Harley flathead motor looks similar to a big-twin Harley flathead motor. The easiest way to tell them apart is that Big-Twin flatheads (UL and VL) have their drive chains on the left, and the 45 has them on the right.
In stock trim, small-twin flatheads are slower, lighter, and less expensive than big-twin flathead models. The two engines do not share many interchangeable parts.
Best Harley Flathead To Restore
In their day, Harley 45 flathead motorcycles were easy to maintain and would continue to run even in the worst of tune. They were simple and efficient, but not particularly powerful in stock trim.
While the big-twin flathead bikes are faster and command more money, the small-twin models are lighter, easier to ride, and easier to kick-start.
******************************
Rocky Horror Motorcycle
In the 1975 film, The Rocky Horror Picture Show, Eddie (played by singer Meatloaf) rides out of the deep freeze of Dr. Frank-N-Furter's lair on a Harley-Davidson WLA.

******************************
Misc Notes
Harley flatheads never needed leaded gas. The reason tetraethyl lead was added to gasoline in the first place was to increase octane for vehicles with high compression. This is not an issue with pre-WW2 motorcycles.
******************************
Related Articles: